In situations where IRR and NPV give conflicting decisions, NPV decision should be preferred. The initial investment outlay represents the total cash outflow that occurs at the inception (time 0) of the project. However, there are several drawbacks to using the payback period to measure potential returns. Input the initial investment amount and discount rate into cells A1 and A2, respectively.
When calculating NPV, what are the factors that need to be taken into account?
Theoretically, we should use the firm’s cost to attract capital as the discount rate when calculating NPV. In reality, it is difficult to estimate this cost of capital accurately and confidently. Because the discount rate is an approximate value, we want to determine whether a small error in our estimate is important to our overall conclusion. We can do this by creating an NPV profile, which graphs the NPV at a variety of discount rates and allows us to determine how sensitive the NPV is to changes in the discount rate. Net Present Value is a critical tool in financial decision-making, as it enables investors and financial managers to evaluate the profitability and viability of potential investments or projects.
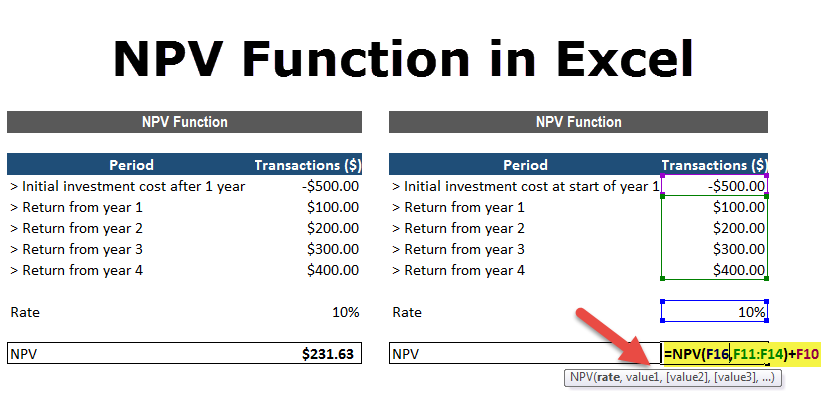
NPV Formula
Net present value is a financial calculation used to determine the present value of future cash flows. It takes into account the time value of money, which means that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar received in the future. If the net present value of a project or investment, is negative it means the expected rate of return that will be earned on it is less than the discount rate (required rate of return or hurdle rate). As long as interest rates are positive, a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because a dollar today can earn an extra day’s worth of interest. Even if future returns can be projected with certainty, they must be discounted because time must pass before they’re realized—the time during which a comparable sum could earn interest.
What is the importance of net present value in financial decision-making?
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets, managed by professionals. In case of standalone projects, accept a project only if its NPV is positive, direct vs indirect costs reject it if its NPV is negative and stay indifferent between accepting or rejecting if NPV is zero. Most financial analysts never calculate the net present value by hand or with a calculator; instead, they use Excel.
Calculate the net present value of the investment if the discount rate is 18%. The simulations can offer insights into how different variables, such as cost and timing of cash flows, can affect the potential returns. Additionally, sensitivity analysis helps to identify which parameters are most sensitive to changes in expected cash flows and, therefore, should be included when making investment decisions. The NPV of a project depends on the expected cash flows from the project and the discount rate used to translate those expected cash flows to the present value. When we used a 9% discount rate, the NPV of the embroidery machine project was $2,836.
In conclusion, Net Present Value is a valuable tool for measuring the potential return on investment of a project or investment. With careful consideration of assumptions and risks, it can be a helpful way to make investment decisions. Finally, NPV is a time-dependent measure and doesn’t consider that cash flows may not all be received simultaneously.
- The benefits of using NPV as a measure of returns include accuracy and comprehensiveness.
- Therefore, when evaluating investment opportunities, a higher NPV is a favorable indicator, aligning to maximize profitability and create long-term value.
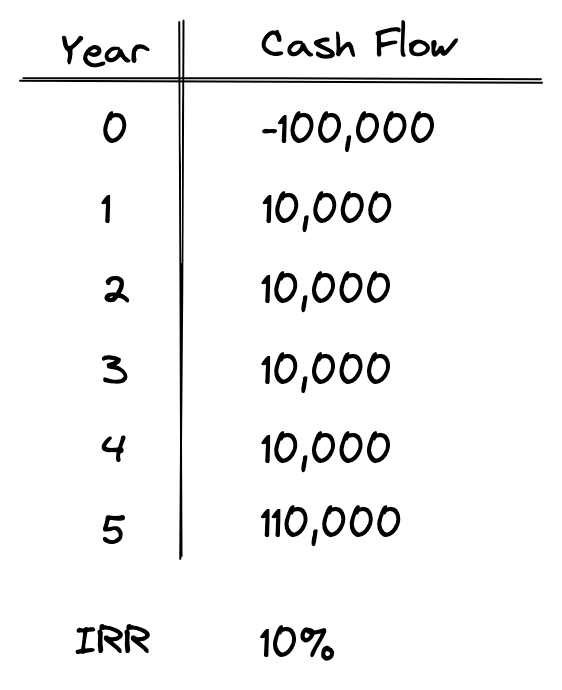
- As the discount rate becomes larger, the NPV falls and eventually becomes negative.
- If the money is received today, it can be invested and earn interest, so it will be worth more than $1 million in five years’ time.
The present value is calculated by discounting future cash flows using a discount rate that reflects the time value of money. Net present value (NPV) of a project represents the change in a company’s net worth/equity that would result from acceptance of the project over its life. It equals the present value of the project net cash inflows minus the initial investment outlay. It is one of the most reliable techniques used in capital budgeting because it is based on the discounted cash flow approach. The benefits of using NPV as a measure of returns include accuracy and comprehensiveness.
In practice, the XNPV Excel function is used to calculate the net present value (NPV). At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Using the discount rate, calculate the present value of each cash flow by dividing the cash flow by (1 + discount rate) raised to the power of the period in which the cash flow occurs. This calculation will provide the present value of each cash flow, adjusted for the time value of money. To value a project is typically more straightforward than an entire business.
The disadvantage of NPV approach is that it is more complex than other methods that do not consider present value of cash flows. Furthermore, it assumes immediate reinvestment of the cash generated by projects being analyzed. This assumption might not always be appropriate due to changing economic conditions. If you are confident that the firm’s cost of attracting funds is less than 14%, the company should accept the project. If the cost of capital is more than 14%, however, the NPV is negative, and the company should reject the project.